How We Built A Zero Energy Building: A Case Study
Nest-In from the house of Tata Steel is leading India’s shift towards environmentally responsible construction by showcasing how climate-ready homes can be designed and delivered efficiently. With rising energy consumption and increasing climate pressures, there is a growing need for residential buildings that use less energy and operate responsibly throughout their lifespan.
The Zero Energy Home built by Nest-In in Bhubaneswar demonstrates how modern engineering, thoughtful design and steel-based construction can create a truly sustainable home that produces as much energy as it consumes, reflecting the principles of a zero energy building and supporting India’s long-term sustainability goals.
Understanding a Zero Energy Building
A net zero energy building is designed to balance its annual energy consumption through a combination of passive design strategies, efficient systems and on-site renewable generation. Nest-In's ZEB project stands out as a practical example. Built in 3.5 months and spanning 1,836 sq. ft., the home is constructed using Light Gauge Steel Framing (LGSF) technology, which enables faster construction while delivering a strong, durable structure that performs reliably across varying weather conditions.
This project contributes meaningfully to India’s growing landscape of zero energy buildings, demonstrating how energy-resilient homes can be adapted to local climates, user needs and long-term sustainability goals.
What Makes It Net Zero?
- Climate Resilient Design
- Energy Efficient Design
- Renewable Energy Integration
- Smart Energy Management
A Climate-Responsive Design Approach
The Zero Energy building is designed to adapt as household needs evolve. With an LGSF framework, modular components, multifunctional spaces, and non-permanent partitions, it allows easy reconfiguration, scalability and long-term flexibility.
The building's design is rooted in climate intelligence, crafted specifically for the warm-humid conditions of Bhubaneswar. Extensive climate simulations informed the placement of openings, verandahs and shading elements, while the architecture leverages controlled daylight, natural ventilation pathways and climate-responsive massing to minimise cooling demand.
Materials That Make a Difference
Each material and finish in the home is chosen to harmonise aesthetics, performance and sustainability. The structure incorporates insulated walls, fibre cement boards, gypsum boards, cool roofs, and high-performance glazing. These choices contribute to a strong envelope that helps limit unwanted heat from entering the home, reducing the need for mechanical cooling and supporting the project’s wider goals of sustainable construction.
Technology Integration and Smart Systems
Every system in the home is chosen to optimise efficiency and comfort. A high-efficiency Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) heating, ventilation and air conditioning system adjusts cooling based on actual usage needs, helping the home maintain consistent indoor conditions while using energy more efficiently in Bhubaneswar’s warm and humid climate. LED lighting, designed with the potential for daylight-linked dimming, reduces operational demand.
On-site renewable generation is enabled through rooftop solar and façade-integrated photovoltaics system, which embeds solar cells directly into the structure of the building. Together, they support the principles of carbon-neutral buildings by enabling the home to produce clean energy that offsets its annual consumption.
The Role of LGSF in a Zero Energy Building
Light Gauge Steel Framing (LGSF) strengthens a zero-energy building through its durability, sustainability, and long-lasting performance. Prefabricated components ensure precision, enable rapid assembly and reduce on-site effort and energy use, making LGSF a preferred choice for low-carbon, future-ready construction. Its high recyclability further supports a circular approach, reinforcing the building’s overall sustainability footprint.
Key Advantages of LGSF
- Strength and durability
- Lightweight and consistent quality
- Quick and efficient construction
- Recyclability
- Design flexibility
- Easy transportation and handling
These advantages make LGSF a highly adaptable system that supports both performance and sustainability across the building’s lifecycle.
Environmental Impact Across the Building’s Life
The Zero Energy Building is designed to maintain a very low operational energy profile. Passive cooling, efficient systems and solar energy generation work together to reduce dependence on external electricity supply.
Careful material selection and reduced construction waste help cut carbon emissions generated throughout the construction process, lowering the project’s overall environmental impact. The home’s reliance on steel improves recycling opportunities and contributes significantly to lifecycle sustainability.
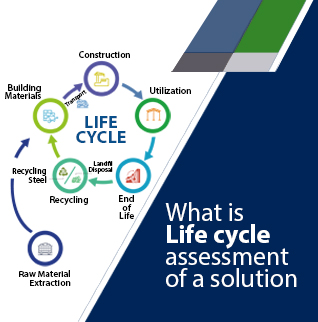
Mapping the Life Cycle Carbon Assessment
A detailed Whole Life Carbon Assessment (WLCA) evaluates the project through its construction, operation and end-of-life stages. Embodied carbon is primarily associated with the LGSF superstructure and material finishes, while operational carbon remains extremely low due to passive design strategies, renewable energy generation, and efficient systems.
End-of-life strategies focus on material recovery and reuse, where the recyclability of steel offsets a significant portion of the embodied footprint. This approach reflects the direction of carbon-neutral buildings, where sustainability is measured across the structure’s entire lifespan.
Conclusion
The Zero Energy Building in Bhubaneswar demonstrates how thoughtful engineering, climate-responsive design and advanced steel-based construction can shape the future of construction in India. By generating its own energy and maintaining a low environmental footprint, the home serves as a blueprint for sustainable living that is resilient, adaptable and ready to be scaled across the country.
To explore sustainable and future-ready building solutions, connect with us at 1800 208 8200 or visit www.nestin.co.in.
Posted in Nest-In on Dec 06, 2025.
Contact Us
Recent Post
How We Built A Zero Energy Building: A Case Study
Zero Energy Building: Redefining India’s Energy-Efficient Future
Addressing the Demand for Durable, Long-Lasting Infrastructure
Rapid Response Infrastructure: Building Fast When Time Matters
Reduce Construction Pollution with Prefab: A Cleaner Way to Build
Category
- Nest-In 104
- HabiNest 65
- MobiNest 122
- Nestudio 28
- EzyNest 21
- Smart EzyNest 6
- ChargeNest 7
- Covid Offerings 4
- Brand 7


































































































































































































































































































Add comment